Munger Lab
Virus-Host Interactions that Determine Infectious Outcomes

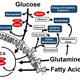
Representation of the cellular metabolome.
(Modified from the KEGG Pathway Database)
View image enlargement
A major focus of our laboratory is human cytomegalovirus (HCMV), a herpes virus, which is the leading cause of congenital viral infection, occurring in approximately 1% of all live births. Congenital HCMV infection results in central nervous system damage in the majority of symptomatic newborns. HCMV infection also poses a serious health risk to immunosuppressed individuals, increasing morbidity in the elderly and in patients receiving immunosuppressive chemotherapy, including cancer patients, transplant recipients, and AIDS patients.
The majority of the projects in our lab study the interfaces between viruses and the host cell that determine the outcome of infection. Specifically, we focus on how viruses usurp cellular metabolic controls and subvert cellular anti-viral signaling to support productive infection. The goal of our laboratory is to increase our mechanistic understanding of these processes to identify novel avenues for therapeutic intervention that could prevent virally-associated pathogenesis.
- Cellular antibody affinity-based CRISPR Screening identifies JUNB as a broadly acting anti-viral factor.; bioRxiv : the preprint server for biology. 2025 Jun 13.
- Taurine from tumour niche drives glycolysis to promote leukaemogenesis.; Nature. 2025 May 14.
- RAF1 promotes successful human cytomegalovirus replication and is regulated by AMPK-mediated phosphorylation during infection.; Journal of virology. 2025 Feb 04.
- A whole food, plant-based diet reduces amino acid levels in patients with metastatic breast cancer.; Cancer & metabolism; Vol 12(1), pp. 38. 2024 Dec 19.
- Catabolism of extracellular glutathione supplies amino acids to support tumor growth.; bioRxiv : the preprint server for biology. 2024 Oct 11.
- The Lactate Receptor GPR81 is a Mechanism of Leukemia-Associated Macrophage Polarization in the Bone Marrow Microenvironment.; bioRxiv : the preprint server for biology. 2024 Aug 16.
News
Affiliations
- Biochemistry & Biophysics
- Microbiology & Immunology
- Center for Biomedical Informatics
- James P. Wilmot Cancer Center
- NIH T32 Training Grant in Cellular, Biochemical & Molecular Sciences
- NIH T32 Training Grant in Immunology
- Biochemistry & Molecular Biology Ph.D. Program
- Biophysics, Structural & Computational Biology Ph.D. Program
- Immunology, Microbiology, and Virology Ph.D. Program
December 4, 2023
Joshua Munger Receives Outstanding Graduate Program Director Award
June 12, 2020
Cancer Investigators Pivot, Take on Coronavirus Research
August 1, 2019
Chris Goodwin Successfully Defends His Thesis
August 16, 2017
Biochemistry Graduate Students Sierra Fox and Chris Goodwin Explain CRISPR Gene Editing on YouTube
Contact Us
Munger Lab
MC 3-7544
601 Elmwood Ave
Rochester, NY 14642
(585) 271-2683