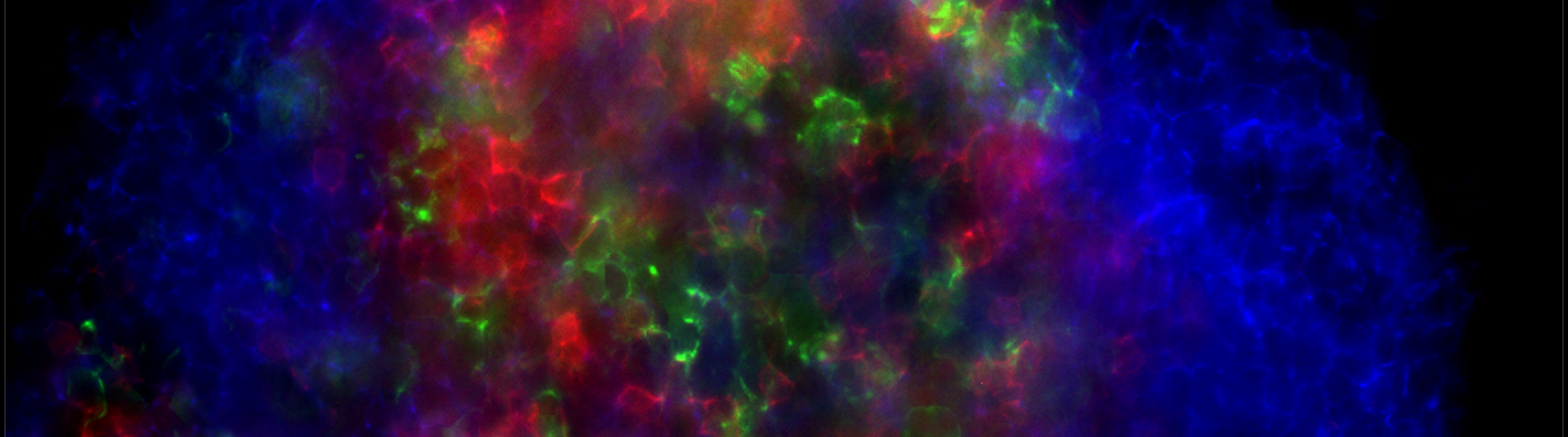
Gerber Lab
Welcome to the Gerber Laboratory
The Immune System and Cancer
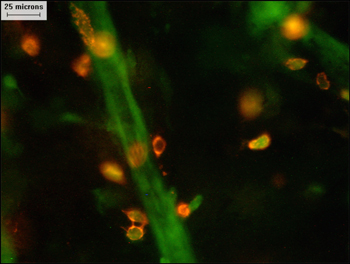
Immune cells (orange) and blood vessels (green) inside of the tumor
The immune system frequently protects us by destroying invading microorganisms such as viruses and bacteria, but is often ineffective in recognizing and combating cancer. Interestingly, immune cells are very capable of finding and killing cancerous cells, but tumor cells are unique in that they can transform immune cells to elicit tumor-promoting functions and ultimately diminish the response to cancer. The Gerber laboratory focuses on reversing this process and instead “re-activates” these immune cells to attack and eradicate the tumor. This is accomplished by a new line of cancer treatment called immunotherapy (enhancing the body’s own immune system to fight cancer), which has resulted in remarkable anti-tumor responses. Immunotherapy stands to redefine how clinicians treat tumors and may hold the key to eliminating cancer.
Tumor Microenvironment
A major obstacle blocking the way for effective cancer therapy is the tumor microenvironment. Within the tumor consists a multitude of various components ranging from cancer cells, fibroblasts, blood vessels, immune cells, nerves, bacteria, etc. Cancerous cells “program” the components of the tumor microenvironment to promote the growth of the malignancy through the production and interaction of a very complex milieu of cancer-driving factors. The Gerber lab focuses on understanding the complexities of the tumor microenvironment to identify what factors promote tumor growth and, from this data, develop therapies to counteract these molecules.
Enhancing Cancer Radiotherapy by Targeting the Immune System
 One particular goal of the Gerber laboratory is to enhance the efficacy of radiotherapy. We believe that improving this particular cancer treatment would benefit many cancer patients, as one half of all malignancies are treated with radiotherapy. We accomplish this goal though a close collaboration with a fellow member of the Center, Edith Lord, who helped pioneer the concept that the immune system mediated many of the anti-tumor effects of existing cancer therapies, such as radiotherapy. This work ushered in a paradigm shift in the field and suggests that radiotherapy, an effective cancer treatment modality, can be further enhanced by targeting and stimulating immune cells. Using a state-of-the-art small animal radiation delivery system that recapitulates equipment used in clinical radiation oncology, we have demonstrated that immunotherapy can greatly impact the effectiveness of radiotherapy resulting in unprecedented tumor control and even cures in preclinical models. We have also been fortunate to translate some of our findings into clinical trials and continue to take a “bench to bedside” approach to expedite the development of vital treatments for cancer patients.
One particular goal of the Gerber laboratory is to enhance the efficacy of radiotherapy. We believe that improving this particular cancer treatment would benefit many cancer patients, as one half of all malignancies are treated with radiotherapy. We accomplish this goal though a close collaboration with a fellow member of the Center, Edith Lord, who helped pioneer the concept that the immune system mediated many of the anti-tumor effects of existing cancer therapies, such as radiotherapy. This work ushered in a paradigm shift in the field and suggests that radiotherapy, an effective cancer treatment modality, can be further enhanced by targeting and stimulating immune cells. Using a state-of-the-art small animal radiation delivery system that recapitulates equipment used in clinical radiation oncology, we have demonstrated that immunotherapy can greatly impact the effectiveness of radiotherapy resulting in unprecedented tumor control and even cures in preclinical models. We have also been fortunate to translate some of our findings into clinical trials and continue to take a “bench to bedside” approach to expedite the development of vital treatments for cancer patients.
Research Projects

Enhancing Specialized Radiotherapy with Immunotherapy to Treat Pancreatic Cancer

Crosstalk between the Nervous and Immune Systems within the Tumor
Boosting Anti-tumor Immune Responses by Optimizing Immunogenic Cell Death
Targeting the tumor draining lymph node to promote anti-tumor immunity
Decipher the Role of Granulocytes in Pancreatic Cancer
Selected Publications
Uccello TP, Lesch ML, Kintzel SA, Gradzewicz LB, Lamrous L, Murphy SP, Fleming FJ, Mills BN, Murphy JD, Hughson A, Hannon G, Garrett-Larsen J, Qiu H, Drage MG, Ye J, Gavras NW, Keeley DC, Love TM, Repasky EA, Lord EM, Linehan DC, Gerber SA. New insights into the responder/nonresponder divide in rectal cancer: Damage-induced Type I IFNs dictate treatment efficacy and can be targeted to enhance radiotherapy. Cell Death Dis.2023 Jul 26;14(7):470. doi: 10.1038/s41419-023-05999-3. PubMed PMID: 37495596; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC10372053
Ye J, Mills BN, Qin SS, Garrett-Larsen J, Murphy JD, Uccello TP, Han BJ, Vrooman TG, Johnston CJ, Lord EM, Belt BA, Linehan DC, Gerber SA. Toll-like receptor 7/8 agonist R848 alters the immune tumor microenvironment and enhances SBRT-induced antitumor efficacy in murine models of pancreatic cancer. J Immunother Cancer. 2022 Jul;10(7):e004784. doi: 10.1136/jitc-2022-004784. PMID: 35851308.
Ye J, Gavras NW, Keeley DC, Hughson AL, Hannon G, Vrooman TG, Lesch ML, Johnston CJ, Lord EM, Belt BA, Linehan DC, Eyles J, Gerber SA. CD73 and PD-L1 dual blockade amplifies antitumor efficacy of SBRT in murine PDAC models. J Immunother Cancer. 2023 May;11(5). doi: 10.1136/jitc-2023-006842. PubMed PMID: 37142292; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC10163599
Hannon G, Lesch ML, Gerber SA. Harnessing the Immunological Effects of Radiation to Improve Immunotherapies in Cancer. Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Apr 16;24(8). doi: 10.3390/ijms24087359. Review. PubMed PMID: 37108522; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC10138513.
Mills BN, Qiu H, Drage MG, Chen C, Mathew JS, Garrett-Larsen J, Ye J, Uccello TP, Murphy JD, Belt BA, Lord EM, Katz AW, Linehan DC, Gerber SA. Modulation of the Human Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma Immune Microenvironment by Stereotactic Body Radiotherapy. Clin Cancer Res. 2022 Jan 1;28(1):150-162. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-21-2495. Epub 2021 Dec 3. PubMed PMID: 34862242; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC8738140
Uccello TP, Kintzel SA, Mills BN, Murphy JD, Garrett-Larsen J, Battaglia NG, Rodriguez CJ, Drage MG, Ye J, Love TMT, Johnston CJ, Repasky EA, Qiu H, Linehan DC, Lord EM, Gerber SA. Development of an Orthotopic Murine Model of Rectal Cancer in Conjunction With Targeted Short-Course Radiation Therapy. Adv Radiat Oncol. 2022 Mar-Apr;7(2):100867. doi: 10.1016/j.adro.2021.100867. eCollection 2022 Mar-Apr. PubMed PMID: 35036637; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC8749199
Uccello TP, Lesch ML, Ullman NA, Kintzel SA, Gradzewicz LB, Velagaleti T, Fleming FJ, Mills BN, Murphy JD, Garrett-Larsen J, Qiu H, Drage MG, Ye J, Gavras NW, Johnston CJ, Love TMT, Repasky EA, Linehan DC, Lord EM, Gerber SA. Radiation Therapy Exacerbates Tumor-Promoting Innervation and Nerve Signaling in Rectal Cancer. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2023 Mar 1;115(3):733-745. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2022.09.080. Epub 2022 Oct 4. PubMed PMID: 36202180; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC9898185.
Han BJ, Murphy JD, Qin S, Ye J, Uccello TP, Garrett-Larsen J, Belt BA, Prieto PA, Egilmez NK, Lord EM, Linehan DC, Mills BN, Gerber SA. Microspheres Encapsulating Immunotherapy Agents Target the Tumor-Draining Lymph Node in Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma. Immunol Invest. 2020 Jun 4;:1-16. doi: 10.1080/08820139.2020.1765795. [Epub ahead of print] PubMed PMID: 32498585.
Ye J, Mills BN, Zhao T, Han BJ, Murphy JD, Patel AP, Johnston CJ, Lord EM, Belt BA, Linehan DC, Gerber SA. Assessing the Magnitude of Immunogenic Cell Death Following Chemotherapy and Irradiation Reveals a New Strategy to Treat Pancreatic Cancer. Cancer Immunol Res. 2020 Jan;8(1):94-107. doi: 10.1158/2326-6066.CIR-19-0373. Epub 2019 Nov 12. PubMed PMID: 31719057; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC6946873.
Stereotactic Body Radiation and Interleukin-12 Combination Therapy Eradicates Pancreatic Tumors by Repolarizing the Immune Microenvironment.Mills BN, Connolly KA, Ye J, Murphy JD, Uccello TP, Han BJ, Zhao T, Drage MG, Murthy A, Qiu H, Patel A, Figueroa NM, Johnston CJ, Prieto PA, Egilmez NK, Belt BA, Lord EM, Linehan DC, Gerber SA. Cell reports; Vol 29(2). 2019 Oct 08.
Increasing the efficacy of radiotherapy by modulating the CCR2/CCR5 chemokine axes. Connolly KA, Belt BA, Figueroa NM, Murthy A, Patel A, Kim M, Lord EM, Linehan DC, Gerber SA. Oncotarget. 2016; 7(52):86522-86535. PMCID: PMC5349932
View All PublicationsJanuary 1, 2023
Grant Received from the Sky Foundation
July 13, 2022
Joseph Murphy Thesis Defense
July 12, 2022
Tara Vrooman to Predoctoral Training Program
July 12, 2022
Wilmot Cancer Institute Cancer Microenvironment Pilot Award
Contact Us
Scott Gerber Laboratory
MRBX 2-11001
601 Elmwood Ave
Rochester, NY 14642