Blood Circulation in the Fetus and Newborn
How does the fetal circulatory system work?
During pregnancy, the unborn baby (fetus) depends on its mother for nourishment and
oxygen. Since the fetus doesn’t breathe air, their blood circulates differently than
it does after birth:
-
The placenta is the organ that develops and implants in the mother's womb (uterus)
during pregnancy. The unborn baby is connected to the placenta by the umbilical cord.
-
All the necessary nutrition, oxygen, and life support from the mother’s blood goes
through the placenta and to the baby through blood vessels in the umbilical cord.
-
Waste products and carbon dioxide from the baby are sent back through the umbilical
cord blood vessels and placenta to the mother's circulation to be eliminated.
While still in the uterus, the baby's lungs aren't being used. The baby’s liver isn't
fully developed. Circulating blood bypasses the lungs and liver by flowing in different
pathways and through special openings called shunts.
Blood flow in the unborn baby follows this pathway:
-
Oxygen and nutrients from the mother's blood are transferred across the placenta to
the fetus through the umbilical cord.
-
This enriched blood flows through the umbilical vein toward the baby’s liver. There
it moves through a shunt called the ductus venosus.
-
This allows some of the blood to go to the liver. But most of this highly oxygenated
blood flows to a large vessel called the inferior vena cava and then into the right
atrium of the heart.
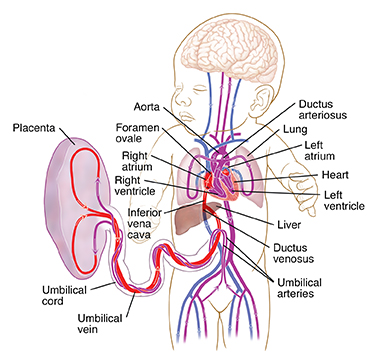
Here is what happens inside the fetal heart:
-
When oxygenated blood from the mother enters the right side of the heart, it flows
into the upper chamber (the right atrium). Most of the blood flows across to the left
atrium through a shunt called the foramen ovale.
-
From the left atrium, blood moves down into the lower chamber of the heart (the left
ventricle). It's then pumped into the first part of the large artery coming from the
heart (the ascending aorta).
-
From the aorta, the oxygen-rich blood is sent to the brain and to the heart muscle
itself. Blood is also sent to the lower body.
-
Blood returning to the heart from the fetal body contains carbon dioxide and waste
products as it enters the right atrium. It flows down into the right ventricle, where
it normally would be sent to the lungs to be oxygenated. Instead, it bypasses the
lungs and flows through the ductus arteriosus into the descending aorta, which connects
to the umbilical arteries. From there, blood flows back into the placenta. There the
carbon dioxide and waste products are released into the mother's circulatory system.
Oxygen and nutrients from the mother's blood are transferred across the placenta.
Then the cycle starts again.
At birth, major changes take place. The umbilical cord is clamped, and the baby no
longer receives oxygen and nutrients from the mother. With the first breaths of air,
the lungs start to expand, and the ductus arteriosus and the foramen ovale both close
over the first minutes and days of life. The baby's circulation and blood flow through
the heart now function like an adult's.