Neck Pain
What is neck pain?
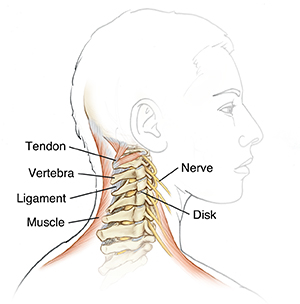
Due to its location and range of motion, your neck is often left unprotected and at
risk for injury. Neck pain can range from mild discomfort to disabling, chronic pain.
What causes neck pain?
Many different things can cause neck pain, including injury, age-related disorders,
and inflammatory disease. Causes of neck pain and problems may include:
-
Damage to the muscles, tendons, or ligaments
-
Herniated disk in the neck
-
Arthritis, such as osteoarthritis or rheumatoid arthritis
-
Cervical (neck) disk degeneration
-
Problems of the vertebrae and bones present at birth (congenital)
-
Tumors
What are the symptoms of neck pain?
Neck pain may feel:
-
Tender
-
Sharp
-
Stiff
-
Burning or tingling
Sometimes other symptoms occur along with neck pain, such as headaches or weakness
in your arm or hand. Pain can also spread to your back.
How is neck pain diagnosed?
Along with a complete medical history and physical exam, diagnostic procedures for
neck pain may include:
-
Blood tests. These tests can help diagnose underlying inflammatory disease.
-
Electromyogram (EMG) and nerve conduction studies. These tests are done together to evaluate nerve function.
-
X-ray. This is a test that uses electromagnetic energy beams to make images of bones.
-
MRI. This procedure uses large magnets and a computer to make detailed images of organs
and structures within the body without the use of X-rays. MRI can often identify damage
or disease of internal structures within a joint or in a nearby ligament or muscle.
-
Computed tomography (CT) scan. This is an imaging procedure that uses X-rays and computer technology to make images
of the body. A CT scan shows detailed images of any part of the body, including the
bones, muscles, fat, and organs. CT scans are more detailed than general X-rays.
How is neck pain treated?
Treatment may include:
When should I call my healthcare provider?
Treatment for neck pain is advised to prevent any future injury or damage. Neck pain
linked to changes in bowel or bladder function, weakness, or loss of sensation can
be a sign of serious injury to the nerves. It should be evaluated right away.
Key points about neck pain
-
Neck pain can range from mild discomfort to disabling, chronic pain.
-
Neck pain can result from many different causes, including injury, age-related disorders,
and inflammatory disease.
-
Getting medical advice as soon as possible after the injury will help reduce future
damage and inflammation.
-
Once you've been treated for the initial injury, you may need a program of physical
rehabilitation. It's important to follow through with your program and exercises to
both build and make muscles stronger that support your activities.
-
Using good body mechanics may prevent future injury.
Next steps
Tips to help you get the most from a visit to your healthcare provider:
-
Know the reason for your visit and what you want to happen.
-
Before your visit, write down questions you want answered.
-
Bring someone with you to help you ask questions and remember what your provider tells
you.
-
At the visit, write down the name of a new diagnosis and any new medicines, treatments,
or tests. Also write down any new instructions your provider gives you.
-
Know why a new medicine or treatment is prescribed, and how it will help you. Also
know what the side effects are and when they should be reported.
-
Ask if your condition can be treated in other ways.
-
Know why a test or procedure is recommended and what the results could mean.
-
Know what to expect if you don't take the medicine or have the test or procedure.
-
If you have a follow-up appointment, write down the date, time, and purpose for that
visit.
-
Know how you can contact your healthcare provider if you have questions, especially
after office hours or on weekends.