Anatomy of the Eye
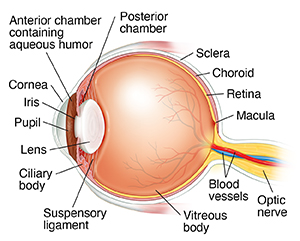
Anterior chamber. The front section of the eye's interior where aqueous humor flows in and out, providing
nourishment to the eye.
Aqueous humor. The clear watery fluid in the front part of the eye known as the anterior chamber.
Blood vessels. Tubes (arteries and veins) that carry blood to and from the eye.
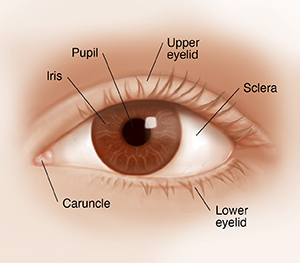
Caruncle. A small, red structure in the corner of the eye closest to the nose that contains
modified sebaceous and sweat glands.
Choroid. The thin layer of blood vessels that lies between the retina and the sclera and supplies
blood to the outer portion of the retina.
Ciliary body. The part of the eye that makes aqueous humor.
Cornea. The clear, dome-shaped surface that covers and protects the front of the eye.
Iris. The colored part of the eye that helps control the amount of light entering the eye.
Lens (crystalline lens). The transparent structure inside the eye that focuses light rays onto the retina,
much like the lens in a camera.
Lower eyelid. Skin that covers the lower part of the eye, including the cornea, when closed.
Macula. The central portion of the retina that allows us to see fine details.
Optic nerve. A bundle of nerve fibers that connect the retina with the brain. The optic nerve carries
signals of light, dark, and colors to a part of the brain called the visual cortex,
which assembles the signals into images and results in vision.
Posterior chamber. The very narrow part of the eye behind the iris and in front of the lens
Pupil. The opening in the center of the iris through which light passes to the back of the
eye.
Retina. The light-sensitive nerve layer that lines the inside of the back of the eye. The
retina senses light and creates impulses that are sent through the optic nerve to
the brain.
Sclera. The white visible portion of the eye. The muscles that move the eye are attached
to the sclera.
Suspensory ligament of lens. A series of fibers that connects the ciliary body with the lens, holding it in place.
Upper eyelid. Skin that covers the upper part of the eye, including the cornea, when closed.
Vitreous body. A clear, jelly-like substance that fills the middle of the eye between the lens and
the retina.