Understanding Spirometry
To diagnose and check asthma, your healthcare provider examines you. They listen to
your lungs in your chest and ask you to breathe. You are asked questions about your
symptoms, triggers, and any family history of asthma or allergies. Lung function tests
may also be done. One of these is a spirometry test.
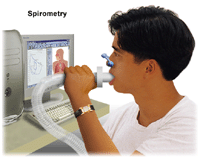
Spirometry is an easy test. It tells your healthcare provider how well your lungs
are working. The test generally takes 15 to 30 minutes. It can be done at a healthcare
provider's office or in a pulmonary function lab. Spirometry is rarely used for children
younger than 6 years.
Your healthcare provider will tell you any special directions before the test. They
may tell you to stop taking certain medicines, not smoke, or not eat a large meal
beforehand. Wear loose, comfortable clothing that allows you to take a big breath.
A trained technician will help with the test. You will sit upright. A nose clip will
be placed on your nose so you only breathe through your mouth. You will put your mouth
around a mouthpiece that is connected to the spirometer.
The spirometer measures the amount of air you breathe out (exhale). It also measures
how quickly you can exhale completely.
Spirometry is a recommended test for people with asthma. It can help with the following:
|
What does it do?
|
When is it usually done?
|
|
It helps diagnose asthma.
|
It may be used when your healthcare provider is making a diagnosis.
|
|
It determines a person’s response to treatment.
|
It may be used after treatment is started and symptoms are more stable.
|
|
It can determine how severe asthma is.
|
It may be used during episodes that get worse or are severe.
|
|
It is used to check asthma.
|
It should be done at least every 1 to 2 years.
|
What does the spirometer measure?
It can take a few different measures of your breath:
-
FVC (forced vital capacity). This is the total amount of air you exhale in a single, long breath.
-
FEV1 (forced expiratory volume in one second). This is the amount of air you exhale in the first second.
-
FEV1/FVC. This is the amount of air exhaled in the first second compared to the total amount
of air exhaled. It’s given as a fraction or a percentage. In general, the higher the
FEV 1/FVC, the better. Normal values depend on your age.
-
PEF (peak expiratory flow). This is a measure of how fast you can exhale. It can be tested with a spirometer
or a peak flow meter.
Talk with your healthcare provider about your test results and what they mean. If
you haven’t had a spirometry test in a year or 2, ask your provider if you should
have it done again.